How to use a Ferrite Core
Ferrite cores are used in various devices as noise suppression components.
In this article, I will explain the know-how for effective use of ferrite cores.
Click here for the video ↓
Ferrite core principle
Ferrite cores are used by attaching them to cables.
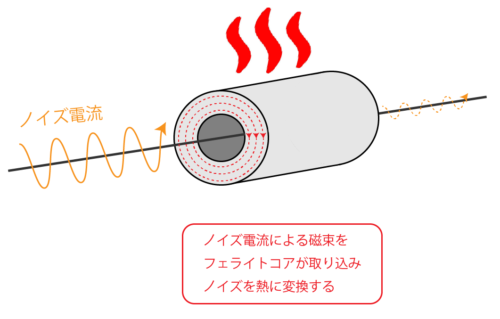
When the ferrite core is attached to the cable, it absorbs the magnetic field generated by the noise current.
Then, noise is suppressed by converting the magnetic field into heat.
This is the principle of noise suppression using a ferrite core.

How to install a ferrite core
It is important to know the mode of noise in order to effectively suppress noise using a ferrite core.
There are two types of noise modes, “normal mode” and “common mode”.
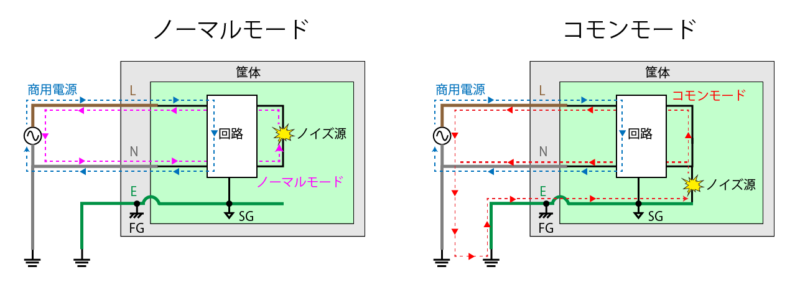
Normal mode noise flows between lines, and common mode noise flows through multiple lines in the same direction.
When using a ferrite core, the mounting method differs depending on the mode.
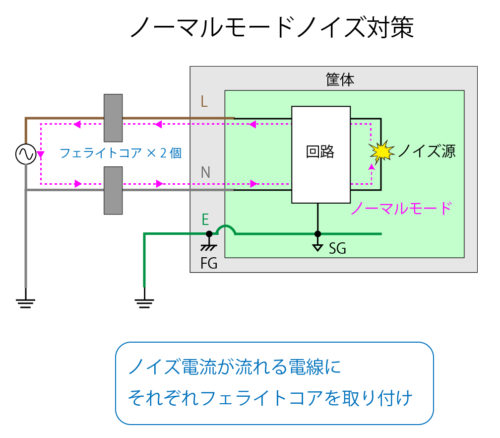
In normal mode, install one ferrite core for each wire through which noise current flows.
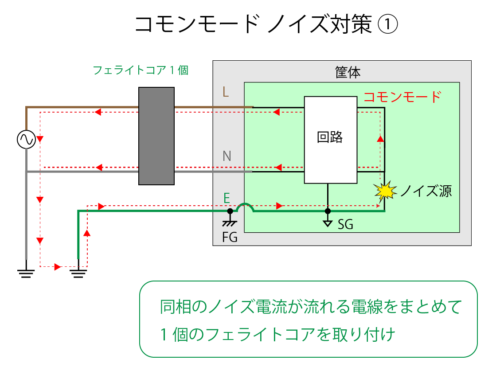
On the other hand, in the common mode, the ferrite core is attached by bundling the wires through which noise current flows.
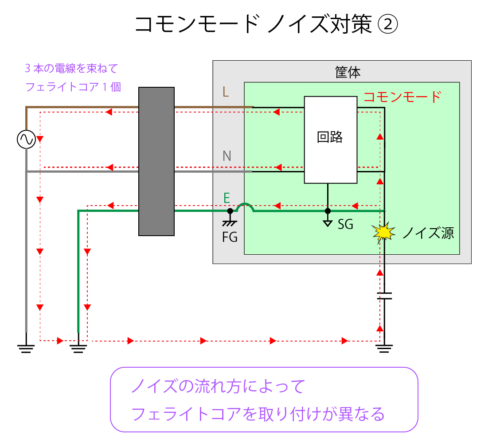
If the noise flow is different, the ferrite core mounting method will change.
How to detect the noise mode
The mode of noise can be detected using a current probe.
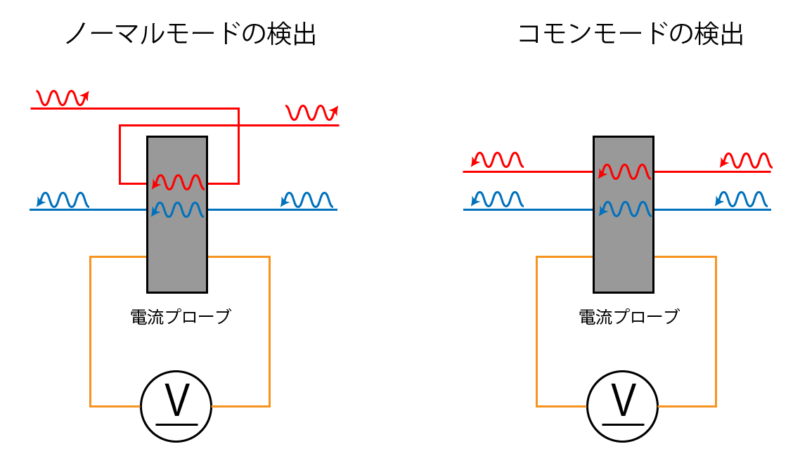
The current probe can also be made by yourself using a ferrite core.
 The requirements for current probes are described in Appendix B of CISPR 16-1-2.
The requirements for current probes are described in Appendix B of CISPR 16-1-2.

Frequency band
The frequency band is important for noise suppression.
Ferrite cores have different frequency characteristics depending on the magnetic material.
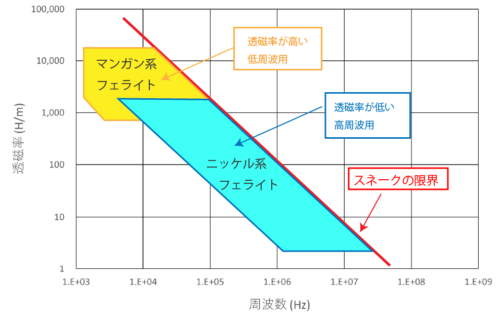
Mn-Zn ferrite core has high magnetic permeability, it suppresses low-frequency noise (1 MHz or less).
Ni-Zn ferrite cores have low magnetic permeability, so they suppress high-frequency noise (1MHz or higher).

Impedance
The higher the impedance, the greater the noise suppression effect.
Therefore, it is important to select a ferrite core with high impedance in the target frequency band.
The impedance of the ferrite core is considered from the two viewpoints of “number of turns” and “size”.
Number of Turns
Ferrite cores are a type of coil.
As the number of turns increases, it looks more like a coil.
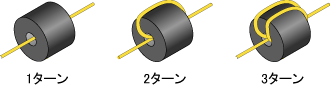 ターン数 出典:北川工業
ターン数 出典:北川工業The number of turns is specified by the number of cables inside the core.
The impedance of the ferrite core is proportional to the square of the number of turns. (In the frequency band below the self-resonant frequency)
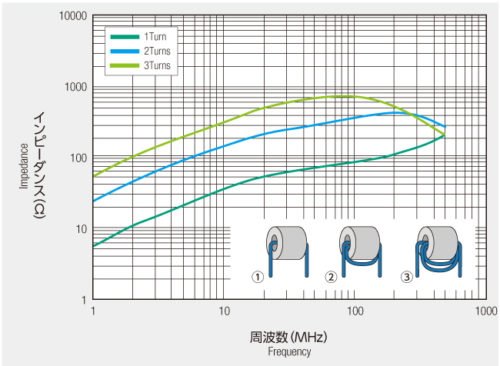 ターン数比較 出典:星和電機
ターン数比較 出典:星和電機Size
Impedance varies depending on the size of the ferrite core.
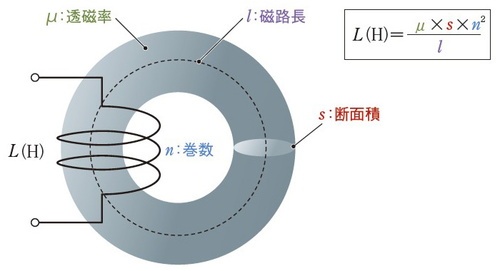 トロイダルコイルのインダクタンス 出典:日経XTECH
トロイダルコイルのインダクタンス 出典:日経XTECHThe parameters related to size are cross-sectional area and magnetic path length.
The larger the cross-sectional area and the shorter the magnetic path length, the higher the impedance.
In other words, the one with a small inner diameter, a large outer diameter, and a long shape has a high impedance.
Summary
I explained the know-how to use ferrite cores effectively.
The basic idea of impedance of a ferrite core is the same as that of a toroidal core.
Therefore, I recommend learning from the basics of toroidal core.
Thank you for reading to the end.